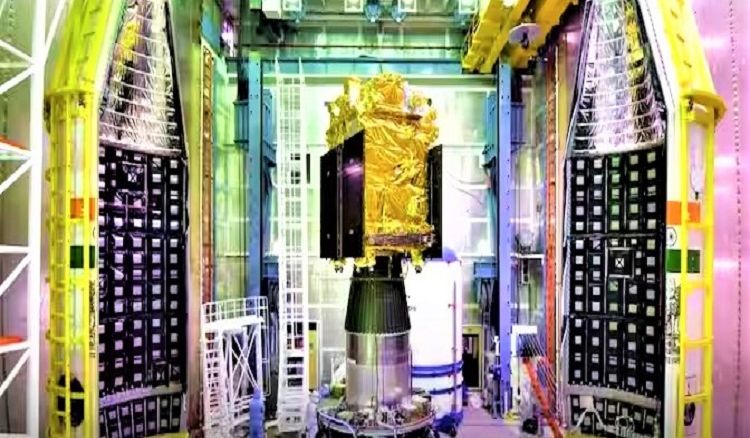
On August 23, India created history by landing on the south pole of the moon. Now it's the turn of the solar expedition. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is sending Aditya-L1 into space on Saturday, September 2. The final preparations are currently underway.
Scientists will observe the sun from a certain distance and conduct research on the sun. India's solar vehicle will conduct surveillance from Lagrange Point. What is this Lagrange point? What is the main purpose of the expedition? All details are shared below.
India's solar launch, Aditya-L1, will depart from Sriharikota Space Centre in Andhra Pradesh at 11:50 a.m. on Saturday. The exposure of the sun's atmosphere will be observed. For that, India's solar spacecraft will stay at Lagrange Point L1. Indian scientists are hopeful that important information about the sun's past, present, and future will be obtained from this expedition. Scientists detailed the 'Lagrange point' at which India's solar spacecraft will be positioned.
What is the Lagrange point? ISRO explained to us that the stable region formed by the mutual attraction and repulsion of two objects like the sun and the earth in space is called the Lagrange point. This Lagrange point is also called the 'parking spot' for the spacecraft because there is less fuel consumption and cosmic activity can be continuously monitored.
To observe the sun, mathematician Joseph Louis Lagrange discovered the 'Lagrange point L1'. According to ISRO, it is possible to observe the sun from Lagrange point L1 without any obstruction. Information about what exactly is happening in the sun's atmosphere and how it affects the overall climate of space can be found without any hesitation.
ISRO said that Aditya-L1 will be launched by a PSLV-C57 rocket. There are a total of seven payloads in Aditya L-1. Those payloads will observe the outer mantle of the sun, the layer of plasma between the sun's surface and the atmosphere, the solar system, and the solar atmosphere. Also, the Aditya-L1 solar probe will use the coronagraph to observe the sun.
What is a CoronaGraph? The coronagraph is an instrument, which is a disc mounted on the solar vehicle. It traps the sun's rays, and the sun's outer mantle emerges within the disc, allowing experiments to be carried out. Without this coronagraph, the sensors of the solar vehicle will not work. The Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) handed over its own Visible Line Emission Coronagraph (VELC) to ISRO. It will be installed in the Aditya-L1 solar vehicle. Apart from this corona graph, the Aditya-L1 spacecraft has six instruments. Four of these will be used to observe the sun remotely. The remaining three will examine the molecules ejected from the sun through solar storms to see what effect they have on the solar system.
Aditya-L1 will be India’s first space-based Indian mission to study the sun, which is the most important source of life on earth. If this mission is successful, ISRO will be able to get closer to the sun and observe it from different perspectives.
 বাংলায় পড়ুন
বাংলায় পড়ুন